November 2022
World Diabetes Day——Access to Diabetes Care
Diabetes Around the World
Diabetes is a chronic, metabolic disease characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose (or blood sugar), which leads over time to serious damage to the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys and nerves [1]. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), there is a continued global increase in diabetes prevalence, with 537 million adults living with diabetes, and the majority living in low-and middle-income countries [2]. This number is expected to rise to 783 million by 2045, which confirms that diabetes is a significant global challenge to the health and well-being of individuals, families and societies.
World Diabetes Day, established in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation with support from WHO, falls on 14 November every year in response to growing concerns about the health and economic threat posed by diabetes.

Effective Approaches to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes
There are effective approaches available to prevent type 2 diabetes and to prevent the complications and premature death that can result from all types of diabetes, including exercising regularly, eating healthily, avoiding smoking, and controlling blood pressure and lipids.
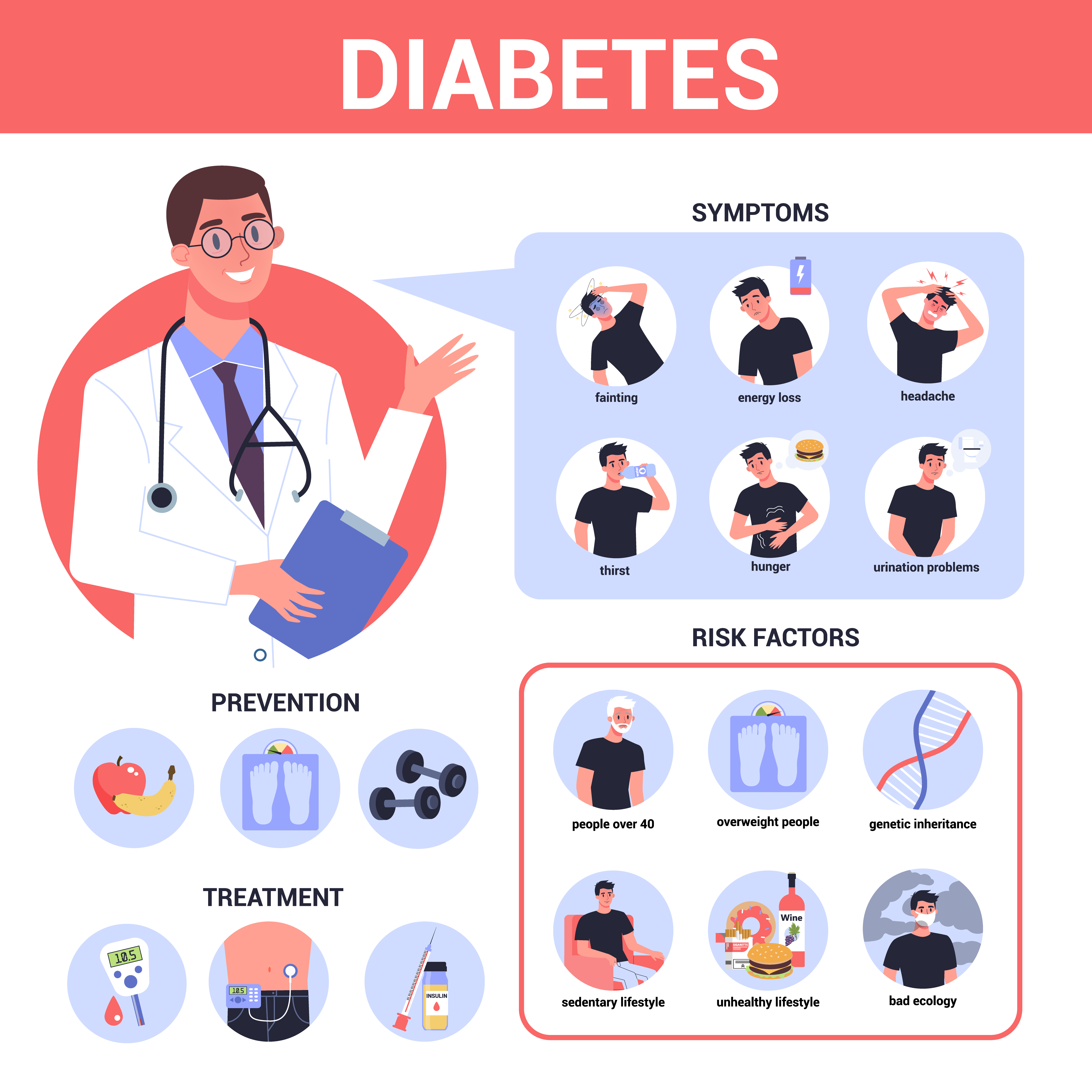
Living Well with Diabetes
Since diabetes may be diagnosed several years after onset, after complications have already arisen, an early diagnosis is important for people who are at high risk of suffering from diabetes-the longer a person lives with undiagnosed and untreated diabetes, the worse their health outcomes are likely to be.
Easy access to basic diagnostics, such as blood glucose testing, should therefore be available in all health care settings.
The American Diabetes Association has recommended glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) as a possible substitute to fasting blood glucose for diagnosis of diabetes [3]. HbA1c is an important indicator of long-term glycemic control with the ability to reflect the cumulative glycemic history of the preceding two to three months. HbA1c not only provides a reliable measure of chronic hyperglycemia but also correlates well with the risk of long-term diabetes complications. Elevated HbA1c has also been regarded as an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease and stroke in subjects with or without diabetes. The valuable information provided by a single HbA1c test has rendered it as a reliable biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of diabetes.
References
1. World Health Organization
2. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edition, International Diabetes Federation, 2021
3. The American Diabetes Association

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.