January 2023
Getein's MAGICL 6000 is a chemiluminescence instrument equipped with a whole blood test module, which has been widely praised by end users worldwide for its small size and fast measurement speed. Compared to traditional laboratory detection methods represented by Sysmex, the MAGICL 6000 HCT module continues to perform consistently and demonstrates excellent correlation in several cardiac markers, showing a great potential for clinical application.
The accuracy and precision of analyte concentrations measured in whole blood by chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA) have been significantly affected by erythrocytes, which leads to poor application of whole blood CLIA in clinical practice. However, the ratio of the packed red blood cell volume to the total volume of blood, known as hematocrit (HCT, %), provides critical information about a patient's health status that helps physicians to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, ailments, and diseases [1–3]. In some emergency situations, if chemiluminescence immunoassay can directly detect whole blood samples, it can significantly reduce the detection time and get earlier and faster treatment for patients.
1. Paper Overview
The paper was published on December 21, 2022 by Dr. Huan Zhao, Southeast University in the journal Biosensors. Biosensors is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal and the Impact Factor is around 5.743.
It compares the correlation between the MAGICL 6000 partial project for the determination of various hematocrit levels in human blood from 0% to 65% by conventional assays and conventional laboratory methods. For whole blood samples, the MAGICL 6000 readout subsystem measures HCT at each sample. the HCT correction is calculated by a software algorithm, and finally, the results for whole blood are accurately reported. The results showed a correlation around 0.9885. Comparison studies using whole blood samples and corresponding plasma samples showed that the square of the correlation coefficients of cTnI, MYO, CK-MB, and NT-proBNP were increased to 0.9992, 0.9997, 0.9996, and 0.9994, respectively, showing a great potential for clinical application.

2. Paper Methods
To address such industry pain points, a chemiluminescence biosensing optical platform for blood hematocrit (HCT) analysis using MAGICL 6000 (Getein Biotechnology, Nanjing, China) was designed. The established HCT detection method for human blood samples reported in this paper requires only 0.1 µL of sample loading without any sample pretreatment, which is much easier than the traditional method.
The biological principles of the procedure are as follows: a certain volume of whole blood samples was lysed with the denaturing agents containing 20 mmol/L CTAB and 1 mol/L ammonium chloride (no pretreatment was required for serum or plasma), and then incubated at 37 ℃ with microparticles coated capture antibodies and acridinium-labeled detection antibodies. The blood samples of 58 healthy people used for HCT analysis approved by Xuzhou Central Hospital Research Ethics Committee.
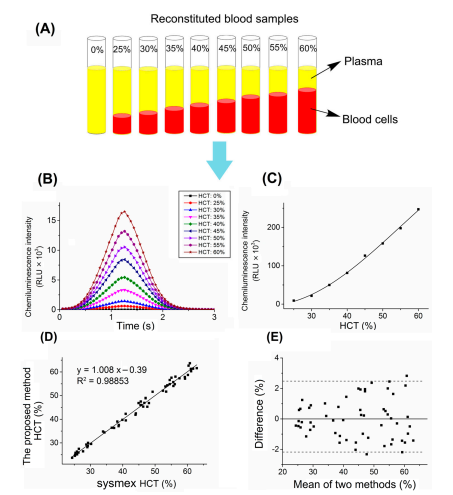
3. Conclusion

In this work, the rapid quantification of blood HCT was successfully completed by a chemiluminescence biosensor using a CLIA-based platform,and the results correlating very well with the clinical analyses (Sysmex XE 5000). The study of HCT influence on cTnI immunoassay indicated that increased HCT impaired immune binding when analyzed in whole blood. With Equation (2) established by a four-parameter logistic curve fit method, the recovery in the whole blood sample was significantly improved.
Combining this HCT measurement and correction with CLIA, which shares the same excitation conditions and photon acquisition device on the MAGICL 6000, we can directly detect the myocardial marker concentrations in the whole blood samples without the need for other HCT measurement instruments. According to the performance analysis, the established method has excellent reproducibility and accuracy due to the advantages of HCT correction, which avoids the influence of erythrocyte inhomogeneity on repeated sampling and excessive cell debris on immune binding.

【Reference】
1. Kosiborod, M.; Smith, G.L.; Radford, M.J.; Foody, J.M.; Krumholz, H.M. The prognostic importance of anemia in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 112–119. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
2. Kosiborod, M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Jones, P.G.; Pitt, B.; Spertus, J.A. The Relationship Between Anemia, Change in Hematocrit Over Time and Change in Health Status in Patients with Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction. J. Card. Failure 2008, 14, 27–34. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
3. Dill, D.B.; Costill, D.L. Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J. Appl. Physiol. 1974, 37, 247–248. [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.