August 2022
Getein PCT solution -- Sepsis diagnosis
Sepsis, defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host-response to infection, is a worldwide highly prevalent syndrome, associated with significant morbidity and mortality[1]. Important aspects of sepsis management are early diagnosis in the first few hours of triage[2]. However, the correct diagnosis and differentiation form non-infectious causes is challenging.
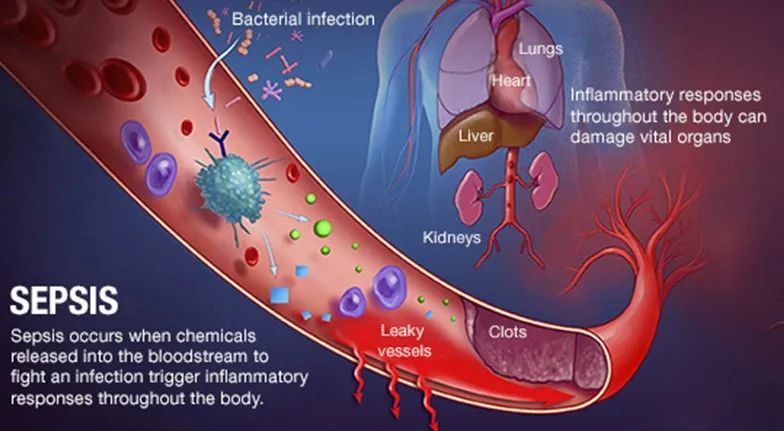
In this regard, the use of blood biomarkers has great potential to improve sepsis care[3]. From a clinical point of view, biomarkers should be able to complement the clinical judgement and interpretation of available prognostic and diagnostic tests, in order to improve patients care[4].
In this context, the use of the host-response and blood infection marker procalcitonin (PCT) has gained much attention and has already been approved for guidance of antimicrobial therapies in patients with respiratory infection and sepsis[5]. PCT is a precursor hormone of calcitonin, that is not detectable in healthy individuals. However, the production of PCT is upregulated in response to bacterial infections and can decrease rapidly during recovery[6]. Thus, PCT provides important additional information, which are able to supplement clinical and diagnostic parameters[7]. This in turn, has not only a high impact on decisions regarding treatment of patients with suspected infections or sepsis[8], but can also influence the duration of antibiotic treatment courses.
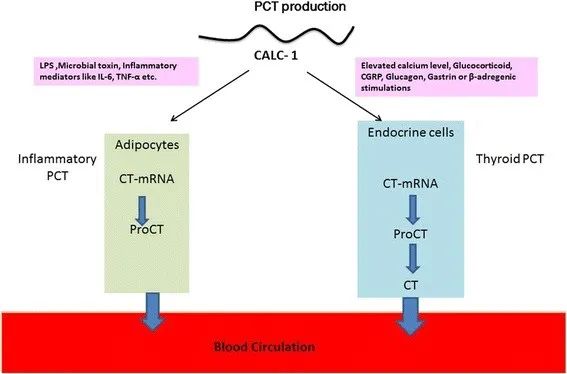
An early diagnosis is still the cornerstones of effective sepsis care. To date, integration of the host-response marker PCT into a comprehensive clinical assessment seems to be a promising approach to reduce diagnostic uncertainties and antibiotic overuse[9]. Still, further research is needed to understand optimal use of PCT, also in combination with other remerging diagnostic tests for most efficient sepsis care.
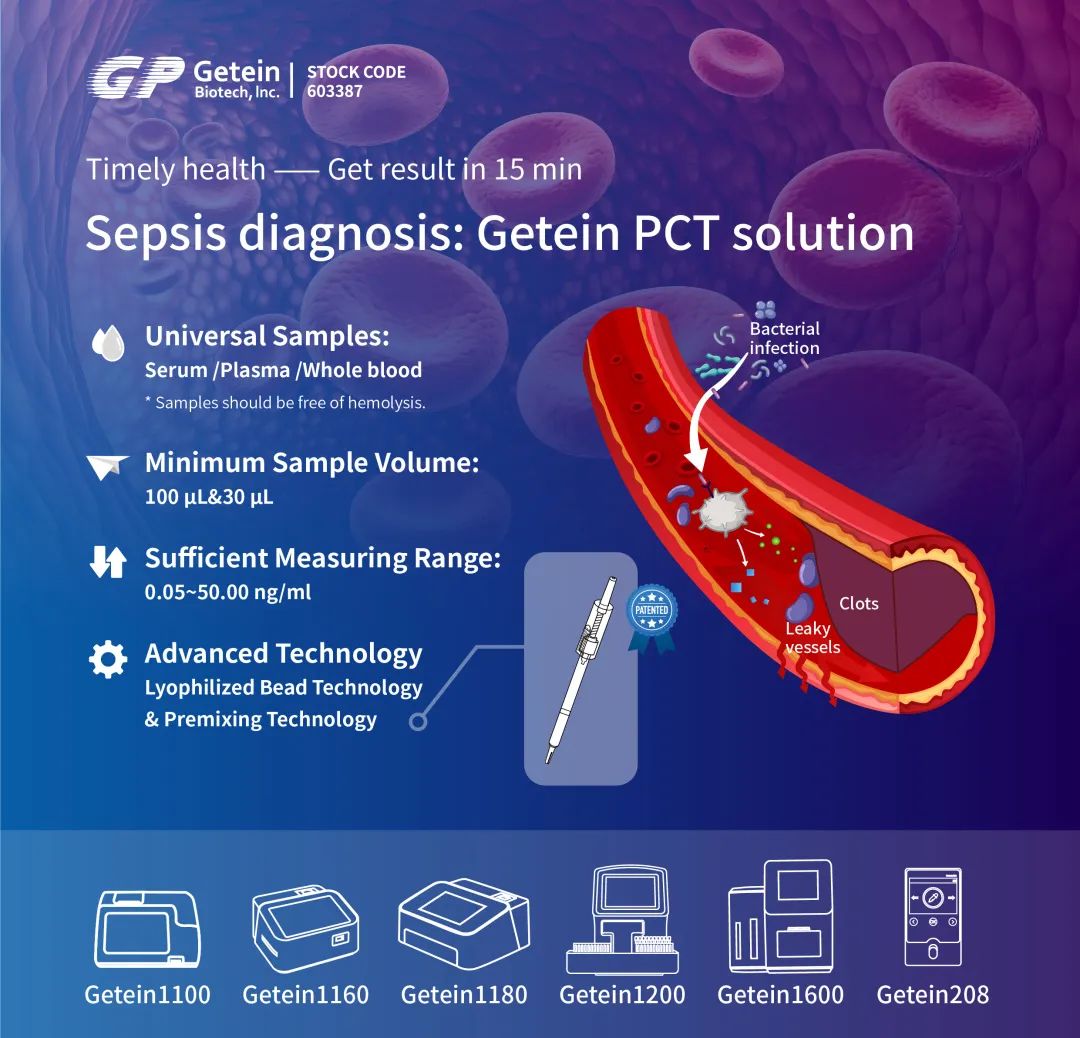
Getein PCT Fast Test Kit is intended for determination of Procalcitonin in human serum, plasma or whole blood samples. The test is used as an aid in the assessment and evaluation of patients suspected of bacterial infection, trauma or shock. The test results are available in just 15 minutes. We also have patented pipette technology to ensure adequate mixing.
Reference:
[1]. Bracht H, Hafner S, Weiss M. Sepsis Update: Definition and Epidemiology.
[2]. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock:
[3]. Schuetz P, Aujesky D, Muller C, et al. Biomarker-guided personalised emergency medicine for all - hope for another hype?
[4]. Schuetz P, Raad I, Amin DN. Using procalcitonin-guided algorithms to improve antimicrobial therapy in ICU patients with respiratory infections and sepsis.
[5]. Lamping F, Jack T, Rubsamen N, et al. Development and validation of a diagnostic model for early differentiation of sepsis and non-infectious SIRS in critically ill children - a data-driven approach using machine-learning algorithms.
[6]. Schuetz P, Birkhahn R, Sherwin R, et al. Serial Procalcitonin Predicts Mortality in Severe Sepsis Patients: Results From the Multicenter Procalcitonin MOnitoring SEpsis (MOSES) Study.
[7]. Mitsuma SF, Mansour MK, Dekker JP, et al. Promising new assays and technologies for the diagnosis and management of infectious diseases.
[8]. Sager R, Kutz A, Mueller B, et al. Procalcitonin-guided diagnosis and antibiotic stewardship revisited.
[9]. Nobre V, Harbarth S, Graf JD, et al. Use of procalcitonin to shorten antibiotic treatment duration in septic patients: a randomized trial.

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.