April 2025
TORCH Screening in Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
Pregnancy is a delicate period, and certain infections can pose serious risks to both pregnant women and newborns. Among these, TORCH infections include Toxoplasma (Toxo), other pathogens (e.g., syphilis), Rubella virus, Cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). These infections are particularly concerning due to their potential to cause congenital defects, developmental delays, and even life-threatening complications in newborns. Understanding TORCH infections, their transmission routes, and prevention strategies is crucial for protecting maternal and neonatal health.
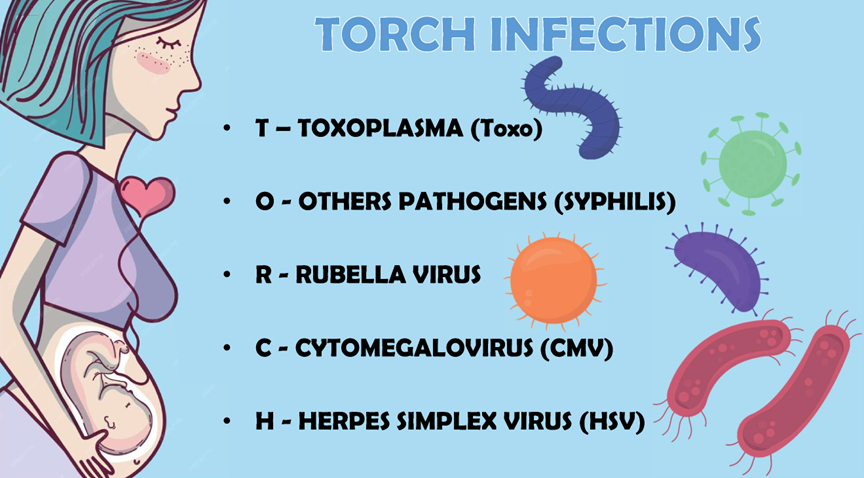
What is TORCH?
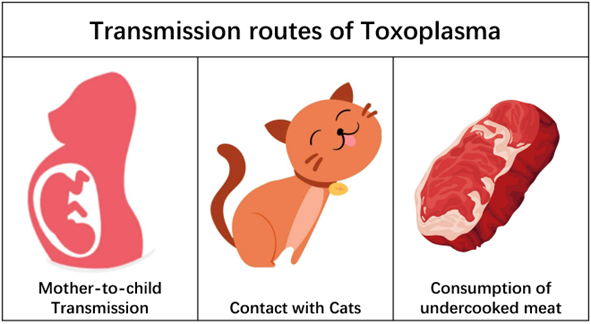
Toxoplasma
Toxoplasma can be transmitted through consuming undercooked, contaminated meat or contact with infected cats and their feces. If a pregnant woman becomes infected, the fetus may suffer severe complications, including miscarriage, preterm birth, or congenital abnormalities. Newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis may experience low birth weight, an enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice, anemia, and neurological damage.
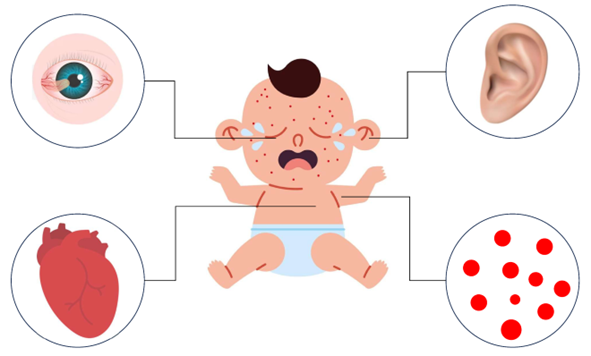
Rubella Virus
Rubella is primarily transmitted to the fetus via the placenta, and the risk and severity of infection depend on the gestational age. During the first 11 weeks of pregnancy, the fetal infection rate is 90%, and the risk of birth defects is nearly 100%. From 11 to 20 weeks, the infection rate drops to 50%, with birth defects occurring in 30% of cases. From 20 to 35 weeks, the infection rate is 37% with no associated birth defects. At 35 to 40 weeks, the infection rate reaches 100%, but congenital anomalies do not occur.Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS) can lead to severe complications. Eye abnormalities include cataracts, microphthalmia, and glaucoma. Congenital heart defects such as patent ductus arteriosus and pulmonary stenosis are also common. Additionally, CRS can cause sensorineural deafness and intellectual disabilities.
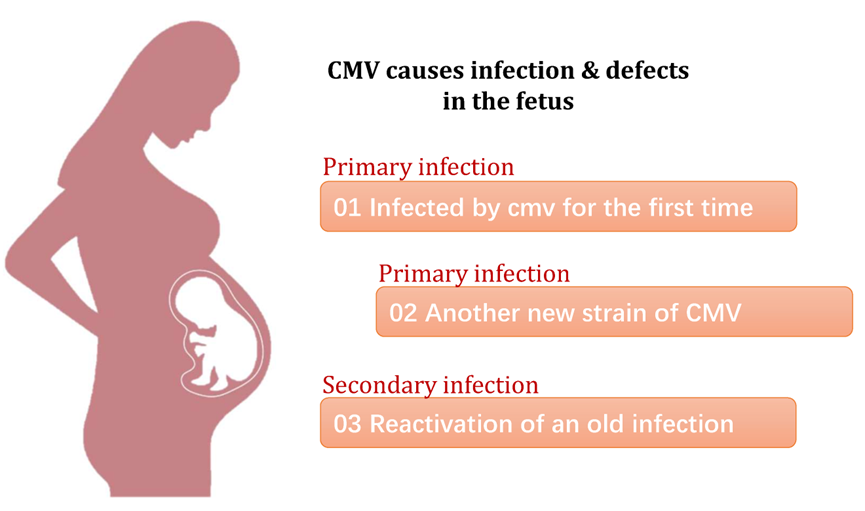
Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) can be transmitted intrauterine, with a 30% fetal infection rate following primary maternal infection, or perinatally during delivery or via breast milk. Among infected fetuses, 40% to 58% suffer permanent damage, including neurological impairments such as intellectual disability, seizures, and motor dysfunction, as well as sensory damage such as hearing loss and retinitis.
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection is primarily transmitted during vaginal delivery (86%), with only 4% transmitted via the placenta. It manifests in three forms: the disseminated form, which affects multiple organs (e.g., hepatitis, jaundice, pneumonia, encephalitis); the central nervous system form, whichcauses meningitis, hydrocephalus, and has a 30% mortality rate; and the localized form, characterized by herpetic lesions in the mouth, eyes, or skin.
Why Choose TORCH IgG/IgM Test?
TORCH IgG and IgM tests are essential for detecting infections during pregnancy and safeguarding the health of both mothers and babies. The TORCH IgG/IgM test includes Toxo IgG, Toxo IgM, Rubella IgG, Rubella IgM, CMV IgG, CMV IgM, HSV IgG, and HSV IgM.
TORCH IgM Positive (+): This may indicate a recent or acute infection. IgM appears early when the body encounters a new infection, which is crucial for detecting infections during pregnancy that could affect the baby.
TORCH IgG Positive (+): This suggests a past infection or immunity. The presence of IgG indicates prior exposure to the infection, with the mother having developed immunity, which offers protection to both mother and baby.
Both TORCH IgM and TORCH IgG Positive (++): This means the mother has recently recovered from a infection and developed immunity, which can help protect the baby from future infections.
Who Should Get Tested?
Preconception Testing: TORCH screening helps assess past infections and reduce the risk of vertical transmission.
Prenatal Screening: First trimester testing is crucial, as fetal organs are developing, and infections at this stage can cause irreversible damage.

High-Risk Groups: Pregnant women with fever or upper respiratory infection symptoms.
Those who have close contact with pets like cats and dogs.
Fetal abnormalities detected by ultrasound (brain calcifications, heart defects).
Exposure to individuals infected with TORCH pathogens.

Getein's Cares for TORCH
CLIA Platform

Getein guides you through TORCH screening for a healthier pregnancy and baby!

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.