January 2025
PCT as an Indicator for Infection Diagnosis
PCT (procalcitonin), as the propeptide of calcitonin (CT), is a glycoprotein consisting of 116 amino acids, with a molecular weight of about 14.5 kDa. Structurally, it can be divided into three parts: the amino terminal, the immature calcitonin and the calcitonin carboxy-terminal peptide. In normal physiological conditions, it is secreted by thyroid C-cells.
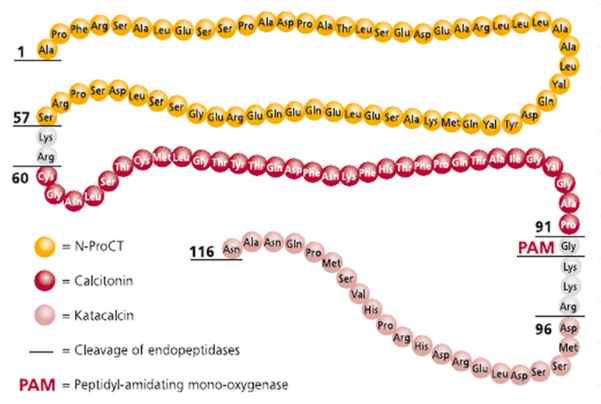
The Production of PCT
The production mechanism of PCT involves multiple factors, including the stimulation by bacterial toxins and inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IFN-γ, TNF-α, etc. These stimuli can induce the transcription of PCT genes and the synthesis of PCT precursors, which are then processed by specific enzymes to generate mature PCT molecules.
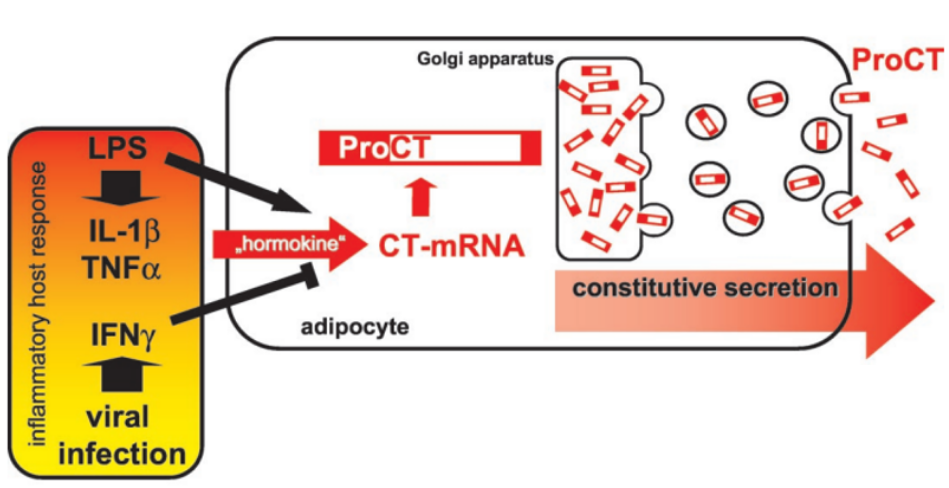
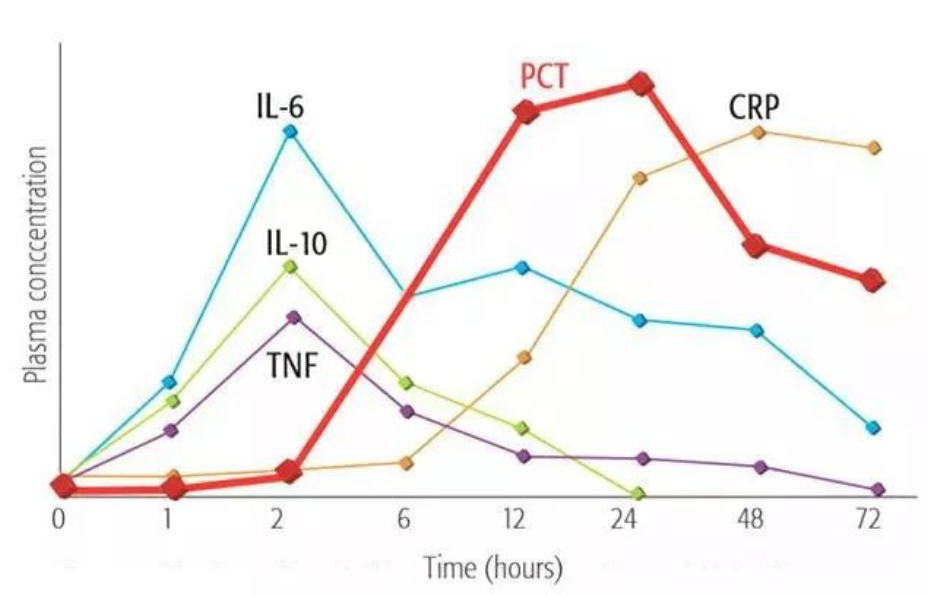
Metabolic Characteristics of PCT
PCT levels can increase within 2-4 hours after infection, reach a peak at 12-24 hours, and remain at a relatively high level within 48 hours. It has good stability in vivo and can be used as an early diagnostic indicator of acute infection.
Clinical Application
Differentiate Bacterial and Non-bacterial Infections
The American Society of Infectious Diseases and the American College of Critical Care Medicine jointly recommend PCT as an auxiliary diagnostic marker to distinguish sepsis from non-infectious systemic inflammatory responses. When bacteria infection causes systemic inflammatory response, the concentration of PCT will increase significantly, while in the case of inflammatory responses such as viral infection, cancer fever, and graft-host rejection, the blood PCT concentration does not increase or only increases slightly.
Guide Antibiotic Treatment
In respiratory tract infections, antibiotics are strongly recommended when PCT > 0.5 μg/L, antibacterial drugs can be used according to the situation when PCT > 0.25 μg/L, and antibacterial drugs should be stopped when PCT < 0.1 μg/L. It is recommended to recheck the PCT concentration 2-3 days after using antibiotics. If the patient's condition fails to improve spontaneously within 6-24 hours after stopping antibacterial drugs, it is suggested to measure the PCT level again. Some studies recommend that in patients with severe respiratory tract infections in ICU, when the initial PCT is very high, if PCT decreases by 80-90% during the treatment with antibacterial drugs, the discontinuation of antibacterial drugs can be considered.
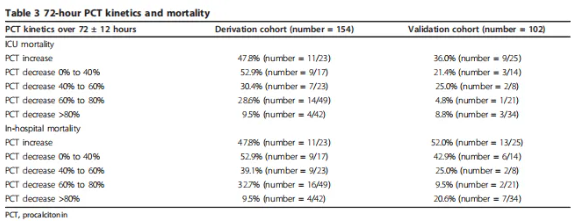
Evaluate the Prognosis of Sepsis Patients
The greater the decline in PCT per unit time, the better the prognosis of the patient. Whether the reduction of PCT reaches 80% is an important predictor of mortality.
Getein’s Solutons for PCT Testing
Currently, both the POCT and CLIA platforms now support the detection of PCT. In the future, Getein will remain dedicated to developing technological and reliable products for the overall well-being of humanity!


Reference
【1】Schuetz P. How to best use procalcitonin to diagnose infections and manage antibiotic treatment. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2022 Nov 2;61(5):822-828. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-1072.
【2】Papp M, Kiss N, Baka M, Trásy D, Zubek L, Fehérvári P, Harnos A, Turan C, Hegyi P, Molnár Z. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy may shorten length of treatment and may improve survival-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 2023 Oct 13;27(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04677-2.【3】Schuetz P, Maurer P, Punjabi V, Desai A, Amin DN, Gluck E. Procalcitonin decrease over 72 hours in US critical care units predicts fatal outcome in sepsis patients. Crit Care. 2013 Jun 20;17(3):R115. doi: 10.1186/cc12787.

Open WeChat and Scan the QR Code. Stay Tuned with Us.